The main function of the endocannabinoid system is that it’s responsible for helping the body maintain a state of homeostasis. In other words, any process that’s self-regulating by which a biological system maintains stability while adjusting to the conditions that ensure its survival.
When the endocannabinoid system is able to function properly, and the state of homeostasis is maintained, the body is able to function properly as well. But, if homeostasis is not maintained, it can lead to many problems and ultimately, the death of an individual.
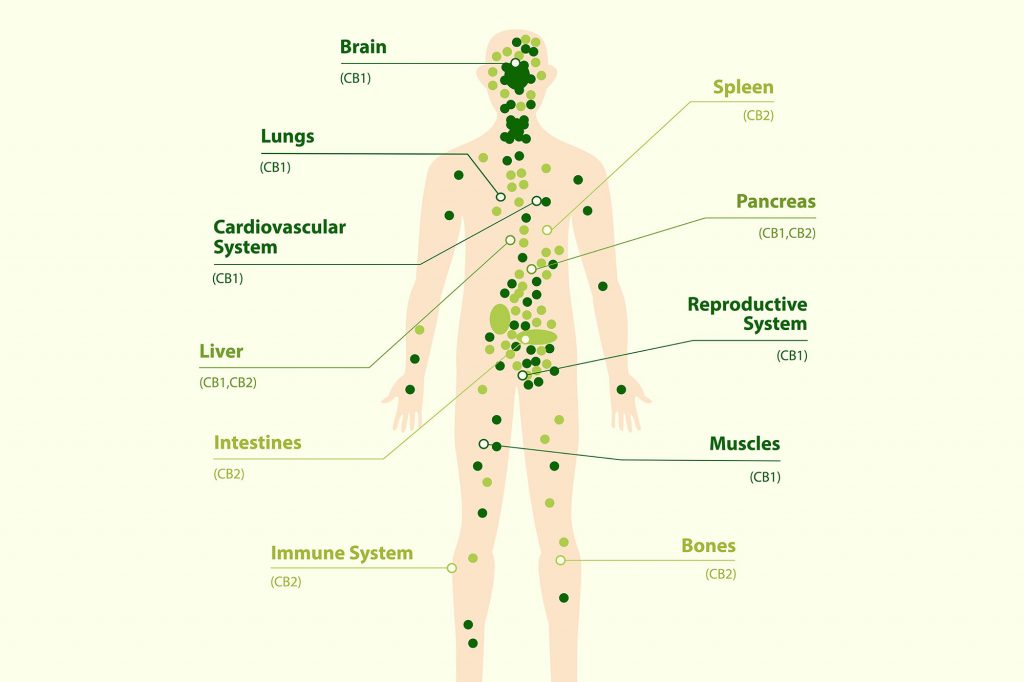
It was discovered in the 1980s, that humans along with some animals synthesize chemical transmitters known as endocannabinoids naturally in the body. The molecules interact with the proteins that are present in our brands and other organs and are known as cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2, or CB1 and CB2.
Along with these receptors being found in the brain and visceral organs, they’re also found in the largest organ of the human body; our skin.
Along with these receptors being found in the brain and visceral organs, they’re also found in the largest organ of the human body; our skin. The CB1 and CB2 receptors are found in nerve endings, sweat glands and the epithelial cells of hair follicles. In other words, these receptors form an intricate network from the deepest to the most superficial cells and tissues in the body.
Hemp And The ECS
Hemp oil/CBD works by binding to CB1 receptors in the body. Unlike THC, which is another type of cannabinoid, hemp molecules don’t bind to the primary binding site of CB1 receptors but at a different location. Since it’s bound by its location, hemp modulates the interaction that occurs with the molecules in the primary binding site. In short, hemp doesn’t have the same psychoactive effects on the endocannabinoid system in the way that THC does.
As mentioned, hemp doesn’t actually attach itself to CB1 or CB2 receptors, instead, it helps stimulate these receptors, causing a reaction without binding to CB1 and CB2 receptors. Additionally, hemp molecules also bind to TRPV-1, which is a protein receptor responsible for regulating pain, inflammation and temperature in the body.
Also, by activating serotonin receptors in the body, hemp has been found to counteract the negative effects of THC.
Hemp And CB2 Receptors
The hemp plant also contains a variety of terpenes that aren’t just molecules associated with the pleasant aromas of plants and flowers. Terpenes also responsible for a physiological function within the endocannabinoid system.
For instance, beta caryophyllene or BCP is one of the most common terpenes that are found in the hemp plant. BCP functions as an activator of the CB2 receptor. This means that full spectrum hemp oils that contain a high quantity of BCP can engage the endocannabinoid system, making it possible for the ECS to regulate brain-body homeostasis which consequently leads to better overall health.